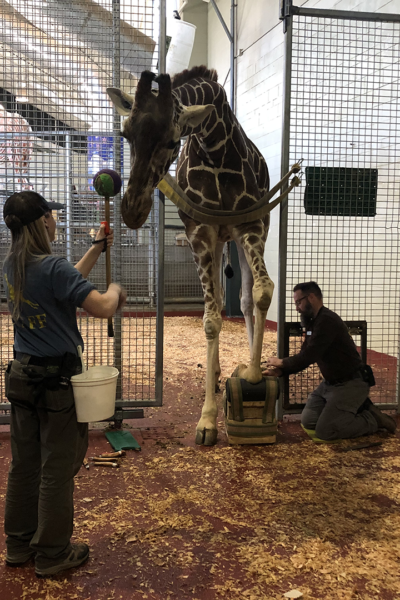
For giraffe, hoof health is vital to overall health. As the zoo profession evolves to further embrace animal husbandry training, and new veterinary technologies allow for better diagnostics, Cheyenne Mountain Zoo is working to improve the future of giraffe care.
“Horses have been domesticated for thousands of years, and the mantra has been ‘no hoof, no horse,’ meaning the overall health of a horse is connected to the health of its hooves. More and more, we’re embracing that for giraffe,” said Dr. Liza Dadone, vice president of mission and programs at CMZoo. “We don’t yet have all the answers, but we have seen that hoof overgrowth changes how the foot supports the weight of a one-ton body. When an animal distributes that much weight differently because of hoof overgrowth, it can have a huge impact on their joints, ligaments and bones.”
Giraffe hooves grow continuously throughout a giraffe’s life. Ongoing hoof maintenance can help prevent issues commonly associated with hoof overgrowth, like lameness and early onset arthritis. Training giraffe to voluntarily participate in hoof maintenance makes preventive care possible, hopefully avoiding these ailments for future generations of giraffe.
Because it’s such an integral part of CMZoo’s work today, some may be surprised to learn that giraffe hoof care is still in its pioneering phase.
“Before our training program started in 2013, we had limited options for managing hoof overgrowth,” said Dr. Dadone. “We also didn’t fully understand what a ‘normal’ giraffe hoof should look like, because we didn’t have consistent access to the underside of the hoof. Training giraffe to participate in their health care has been a total game changer in the level of care we can provide.”
In the last ten years, CMZoo’s Zoo-wide training programs have flourished. The giraffe care team has been recognized nationally for its training success. In just two years, the giraffe care team, led by Animal Care Manager, Jason Bredahl, and Lead Giraffe Keeper, Amy Schilz, developed safety and training protocols and trained the entire herd of giraffe for front foot hoof trims and x-rays.
“It was unheard of,” said Dr. Dadone. “The giraffe were way smarter than we had given them credit for, and this training gave us opportunities to provide ongoing care without anesthesia.”
Hoof care training techniques include asking the animal to voluntarily approach the team, then lift, position and hold its foot so staff can access it safely.
When working around the feet of a 17-foot-tall, one-ton animal, human safety is crucial. The team developed co-working communication that allows one person to train and keep the giraffe’s attention while the other person performs a hoof trim (or other necessary hoof work). Staff learned which kinds of barriers would best protect them and provide adequate access while working safely around giraffe feet. They also studied behaviors in the giraffe so they could recognize when a giraffe might need a break from hoof work.
Once the herd trained to receive x-rays, the care team found that arthritis, ligament injuries, bone damage, and sometimes fractures were present at a rate they weren’t expecting. This discovery led the team to establish a program that included routine front foot x-rays, thermography, visual assessments and monthly hoof trims.
“We can more accurately diagnose and manage giraffe foot health with less invasive procedures, thanks to training,” said Dr. Dadone. “Now that we know giraffe are prone to these issues, we prioritize training of animals from an early age. The goal is that every giraffe, from one year of age, can have its front feet handled and can receive baseline x-rays. The hope is that we can help the next generation of giraffe avoid some of the issues our older giraffe might be experiencing.”
Young giraffe, like Viv, born at CMZoo in July 2019, start training to participate in their care from an early age. Nearly 8-month-old Viv already participates in prerequisite training that will lead to hoof care training. Her keepers say she is shift-trained, which means she will voluntarily move to another area of the barn or outdoor yard when asked. Viv also shifts into ‘the chute,’ which is a narrow part of the indoor barn that some giraffe move through to receive hoof care and other care.
She participates in target training, as well, which means she will touch her nose to a target held by her trainers. For hoof care or x-ray training, target training helps trainers communicate the very specific location the animal is being asked to move to. Likewise, the target helps animals understand what’s being asked of them.
Viv’s keepers have taught her a ‘back up’ command, which helps Viv get into position for hoof care, among other things. They recently started training Viv to get comfortable with being touched, beginning with her shoulders. Once she’s comfortable with being touched on the shoulders, they will continue progress to eventually touch her hooves, which will get Viv even closer to receiving ongoing hoof care.
As CMZoo’s giraffe care team continues finding new ways to improve the health of animals in their care, they learn from and share best practices with the wider giraffe care community. They do this by attending conferences, hosting CMZoo’s annual giraffe care workshops, and through studies, programs and partnerships with Equine Lameness Prevention Organization, Colorado State University Veterinary Teaching Hospital, Giraffe Conservation Foundation and more.

